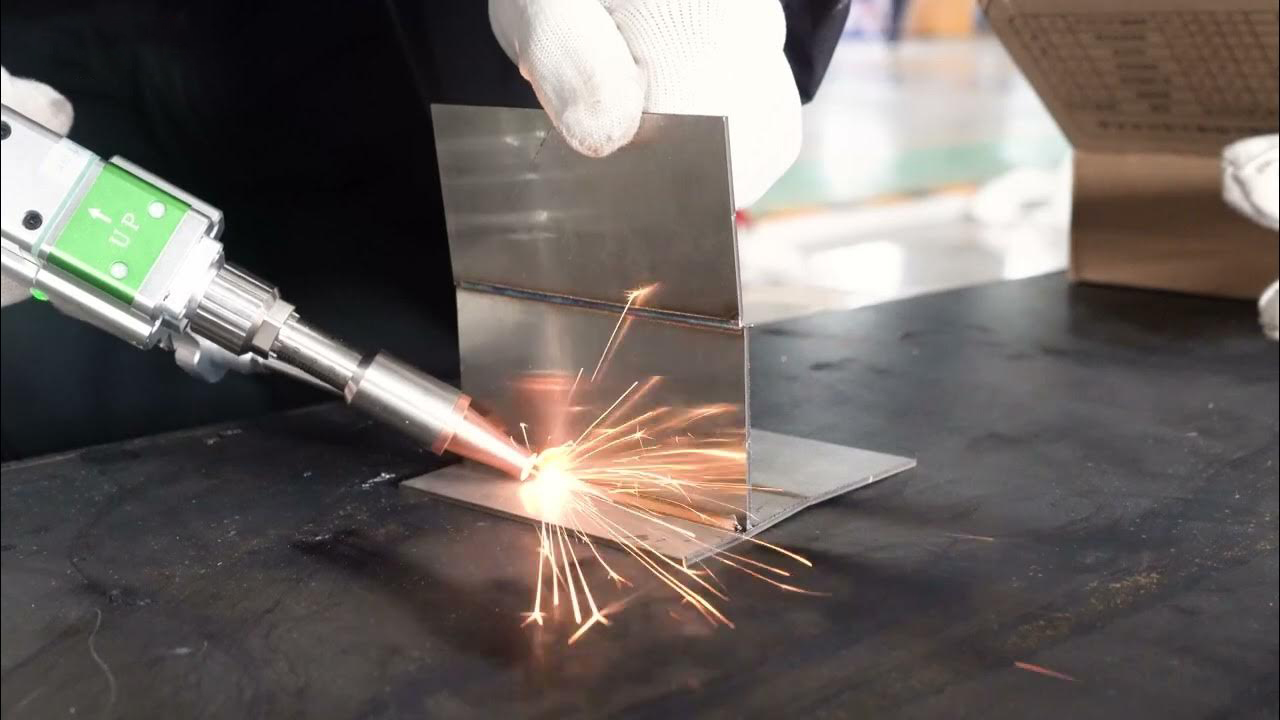

What Is Laser Welding: A Complete Guide to Precision Joining
When it comes to metal joining, few technologies can rival the precision, speed, and versatility of laser welding. But what is laser welding? Imagine a process where materials fuse seamlessly under an intense, focused beam of light—no excessive heat zones, no unnecessary waste, just a clean, accurate weld. Laser welding is redefining craftsmanship across industries, from aerospace to jewelry making.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll dive deep into the process of laser welding, how it works, its key advantages, cost considerations, and emerging trends that could shape its future.
1. What Is Laser Welding?
Laser welding is a technique that uses a concentrated laser beam to melt and join metal or thermoplastic materials. This method allows for high-precision welds with minimal distortion, making it ideal for complex and delicate applications. Unlike traditional welding, laser welding creates a cleaner bond without requiring contact or filler materials in many cases.
2. How Does Laser Welding Work?
The laser welding process involves directing an intense, focused beam of coherent light at the joining area. Here’s a breakdown of how it works:
1.Laser Generation:The laser source, typically a fiber or CO2 laser, emits a high-energy beam.
2.Focusing:The beam passes through a series of lenses that concentrate the energy onto a small focal point.
3.Melting:The concentrated energy melts the metal at the joint, creating a molten pool.
4.Solidification:As the laser moves or stops, the molten pool cools, forming a seamless bond.

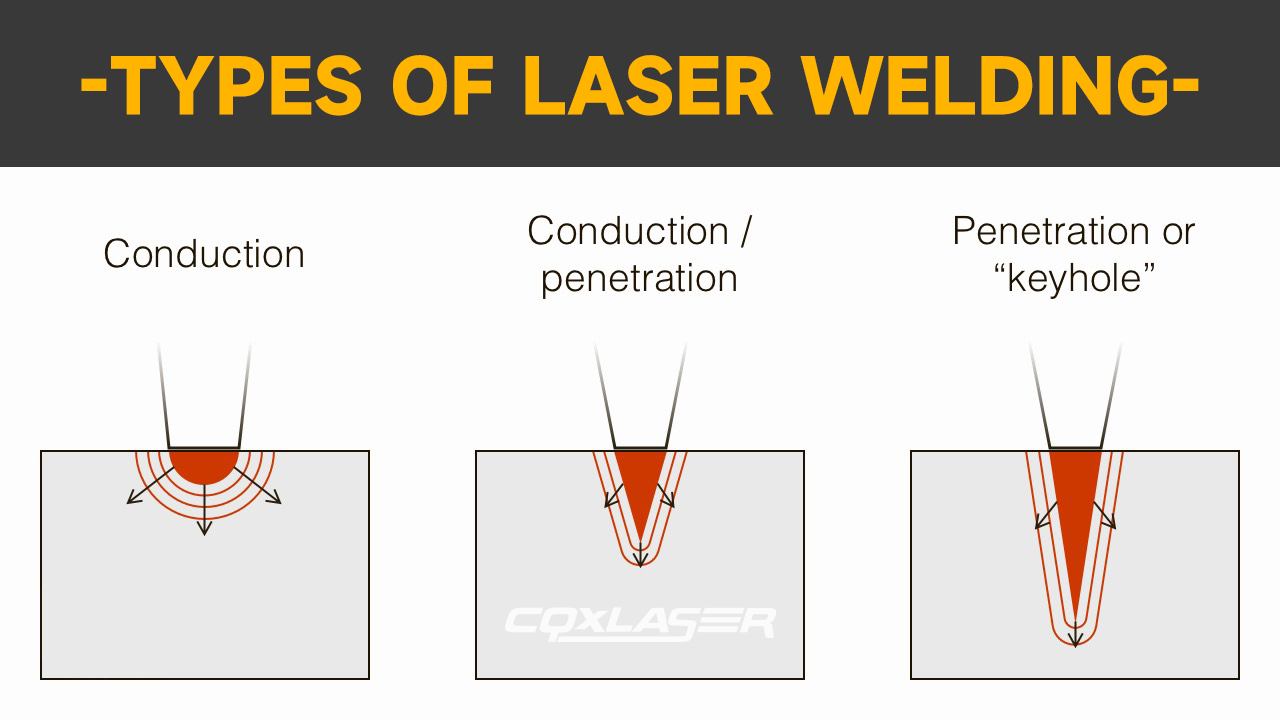
3. Types of Laser Welding Techniques
The laser welding process involves directing an intense, focused beam of coherent light at the joining area. Here’s a breakdown of how it works:
3.1 Keyhole Welding
In keyhole welding, the laser creates a small, deep cavity (or “keyhole”) within the material, allowing for deep weld penetration. This technique is commonly used in high-strength applications, such as aerospace and automotive manufacturing.
3.2 Heat Conduction Welding
This method focuses on heating the surface of the material rather than penetrating deeply. It’s ideal for thin materials and decorative seams that require a smooth, clean finish.
4. Key Advantages of Laser Welding
4.1 High Precision
The concentrated beam allows for pinpoint accuracy, making it possible to weld small, intricate components.
4.2 Minimal Heat-Affected Zones
Traditional welding often creates large heat-affected zones (HAZ), leading to warping and distortion. Laser welding minimizes this by precisely controlling heat input.
4.3 Faster Processing
Laser welding can be up to four times faster than traditional methods, making it ideal for high-volume production lines.
4.4 Versatility
It works with a wide range of materials, including stainless steel, aluminum, copper, and titanium.
4.5 Reduced Post-Processing
The clean welds produced by lasers often require little to no finishing, saving time and labor costs.
5. Common Applications of Laser Welding
5.1 Aerospace Industry
Laser welding is used to join lightweight yet strong materials for critical aircraft components.
5.2 Medical Devices
Precision is key in the production of surgical tools, implants, and other medical instruments, making laser welding the perfect choice.
5.3 Jewelry and Watchmaking
The technology is employed to create flawless seams in fine jewelry and watch casings.
5.4 Automotive Manufacturing
Laser welding is commonly used to join car bodies, engine parts, and exhaust systems with high accuracy and strength.
5.5 Electronics
In the production of microelectronics and sensors, laser welding enables the creation of small, precise joints without damaging delicate components.
6. Cost Considerations
The cost of laser welding depends on several factors, including:
• Type of Laser Source:Fiber lasers tend to be more efficient but also more expensive upfront.
• Power Output:Higher wattage allows for deeper and faster welding but increases the initial investment.
• Automation Level:Manual systems are cheaper, while fully automated systems can be significantly more expensive.
Typical Price Ranges:
• Manual Laser Welders:$8,000 – $15,000
• Semi-Automated Systems:$15,000 – $50,000
• Fully Automated Laser Welding Systems:$50,000 – $500,000+
7. Safety Considerations in Laser Welding
Despite its many advantages, laser welding requires strict adherence to safety protocols:
1.Eye Protection:Wear laser-specific protective goggles to avoid retinal damage.
2.Ventilation:Ensure proper airflow to remove fumes and particulates generated during the welding process.
3.Protective Gear:Use gloves and protective clothing to prevent burns from reflected beams.
8. Comparing Laser Welding to Traditional Welding Methods
| Welding Method | Speed | Precision | Heat-Affected Zone | Post-Processing |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIG Welding | Moderate | Low | Large | High |
| TIG Welding | Slow | High | Medium | Moderate |
| Laser Welding | Fast | Very High | Minimal | Minimal |
Laser welding outperforms traditional methods in terms of speed, accuracy, and overall efficiency, making it a preferred choice for modern manufacturers.
9. Future Trends in Laser Welding Technology
The laser welding industry continues to evolve with advancements that enhance performance and efficiency:
• AI Integration:Artificial intelligence systems optimize welding parameters in real time for improved accuracy and defect detection.
• Portable Laser Welding Systems:Compact, battery-operated models are making on-site welding more accessible.
• Green Lasers:The development of energy-efficient lasers aims to reduce power consumption and environmental impact.

10. How to Choose the Right Laser Welding System
1.Identify Your Application:Determine whether you need the system for small precision work or large-scale production.
2.Evaluate Power Needs:Choose a machine with appropriate wattage based on the materials you’ll be welding.
3.Consider Automation:Decide whether a manual, semi-automated, or fully automated system fits your workflow.
4.Check Support and Warranty:Opt for systems that come with robust after-sales support and comprehensive warranties.
11. Common Questions About Laser Welding
Q: Is laser welding suitable for thick materials?
A: Yes, high-power laser welders can handle thick metal sheets, though the process may require multiple passes.
Q: How long does a typical laser welding machine last?
A: With proper maintenance, most laser welding machines have a lifespan of 10–15 years.
Q: Do laser welders require a lot of maintenance?
A: They require minimal maintenance, typically involving regular lens cleaning and software updates.
Portable laser welders are revolutionizing industries with their blend of precision, mobility, and speed.
By understanding their features, costs, and applications, you can make an informed choice that enhances your productivity and delivers exceptional results.



