Micro Laser Welding: Precision and Innovation for Small-Scale Applications
In the evolving landscape of manufacturing, micro laser welding emerges as a transformative technique. This technology blends precision, versatility, and efficiency, making it indispensable for industries requiring high accuracy in small-scale applications. From medical devices to microelectronics, micro laser welding addresses the challenges of welding tiny components with unmatched precision.
What is Micro Laser Welding?
Micro laser welding is a specialized technique that utilizes a highly focused laser beam to join small and delicate components. This method is engineered to achieve high-accuracy welds with minimal thermal impact, preserving the integrity of the materials involved.
Key characteristics of micro laser welding include:
• Sub-millimeter precision.
• Minimal heat-affected zones (HAZ).
• Compatibility with a wide range of materials, including metals and alloys.
This advanced welding technology is ideal for applications demanding intricate designs and exacting tolerances.
Why Choose Micro Laser Welding?
1. Superior Precision
Micro laser welding offers micron-level accuracy, making it perfect for tiny components where conventional methods fall short.
2. Reduced Thermal Impact
The focused laser minimizes heat spread, reducing distortion and preserving the base material’s properties.
3. Versatility
This technique is compatible with various metals, including stainless steel, titanium, gold, and platinum, as well as dissimilar material combinations.
4. Increased Efficiency
Micro laser welding streamlines production processes, enabling faster assembly without compromising quality.
5. Minimal Post-Weld Processing
The clean welds produced by this method often eliminate the need for extensive finishing or polishing.
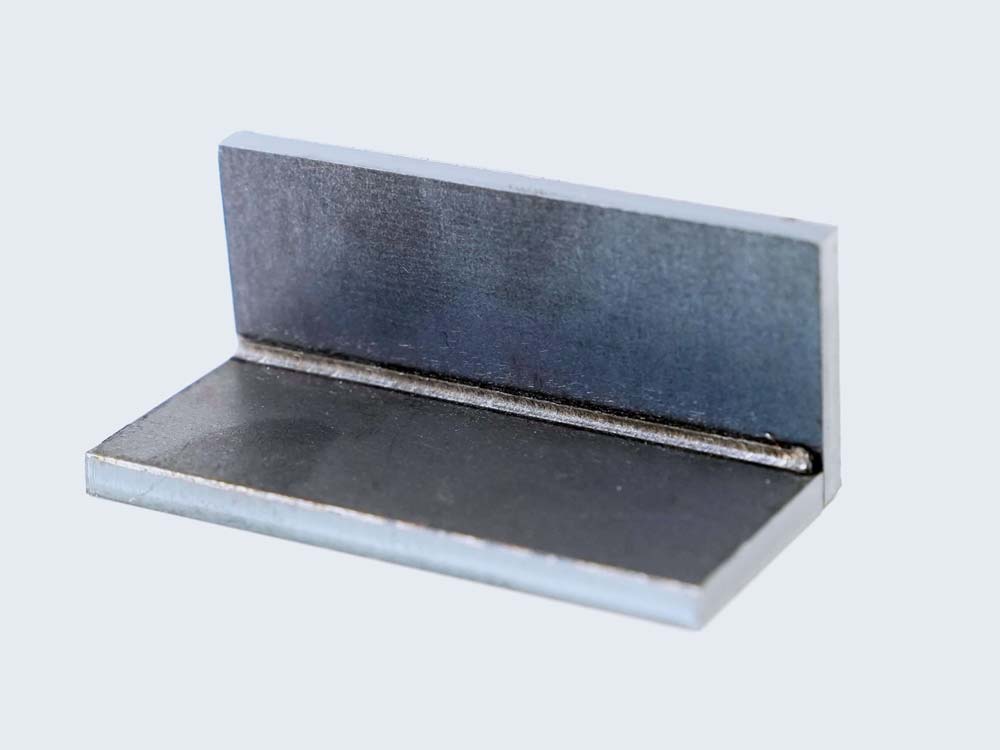

Applications of Micro Laser Welding
1. Medical Device Manufacturing
Micro laser welding is pivotal in creating precision medical instruments, implants, and surgical tools where reliability and sterility are essential.
2. Microelectronics
The intricate circuits and components in microelectronics benefit greatly from the precision and control of micro laser welding.
3. Jewelry and Watchmaking
Artisans rely on micro laser welding for seamless repairs and the creation of intricate designs in jewelry and watches.
4. Aerospace Engineering
In aerospace, this technique is used to fabricate high-precision sensors and instruments.
5. Research and Development
Prototyping and experimental setups often involve micro laser welding for its ability to create accurate and reliable joins.
The Process of Micro Laser Welding
1. Surface Preparation
The materials are cleaned to remove any contaminants that might interfere with the laser’s precision.
2. Laser Setup
The laser’s parameters, including power, focus, and pulse duration, are calibrated to suit the material and application.
3. Welding Execution
The focused laser beam melts and fuses the materials at the joint, creating a seamless and durable bond.
4. Inspection and Testing
Each weld undergoes rigorous inspection to ensure it meets the required tolerances and standards.
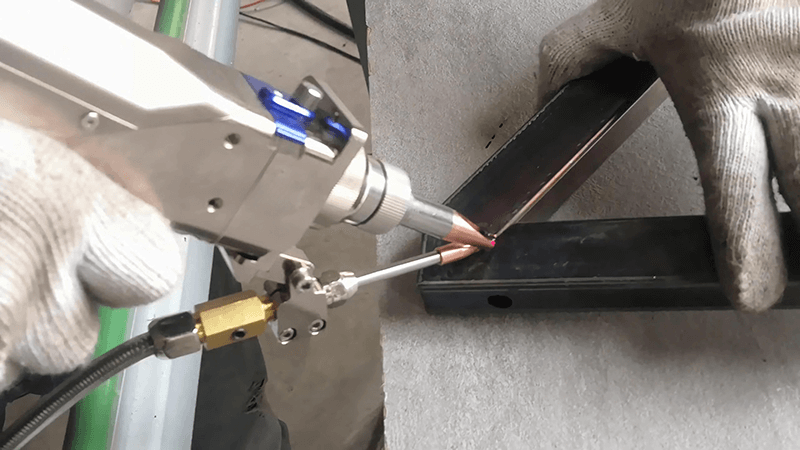
Advantages Over Traditional Welding Methods
1. Precision and Control
Micro laser welding achieves levels of precision that are unattainable with traditional methods like TIG or MIG welding.
2. Non-Contact Process
The laser beam does not physically touch the material, reducing wear on the equipment and the risk of contamination.
3. High-Speed Operation
This method allows for rapid production cycles, enhancing overall efficiency.
4. Compatibility with Miniaturized Components
Traditional welding methods often struggle with small parts, but micro laser welding excels in this domain.

Choosing the Right Micro Laser Welding System
1. Power Output
Lower power levels are typically sufficient for delicate materials, while higher power may be required for thicker components.
2. Beam Quality
A high-quality beam ensures consistent performance and clean welds.
3. User-Friendly Controls
Advanced systems with intuitive interfaces allow for precise adjustments and increased productivity.
4. Safety Features
Built-in safety measures, such as automatic shutoff and shielding, are essential for protecting operators.
Safety Considerations
Protective Measures
Operators should wear laser-rated eyewear and ensure that the welding environment is free from reflective surfaces.
Ventilation Systems
Proper ventilation is necessary to disperse any fumes or particulates generated during the welding process.
Training Requirements
Thorough training is critical to ensure safe and efficient operation of micro laser welding equipment.
Economic and Environmental Impact
1. Cost Efficiency
While the initial investment in micro laser welding equipment can be significant, the long-term savings in time, materials, and labor are substantial.
2. Sustainability
This technique aligns with green manufacturing initiatives by minimizing waste and reducing energy consumption.
3. Reduced Material Waste
The precision of micro laser welding ensures that materials are used efficiently, reducing scrap and excess.
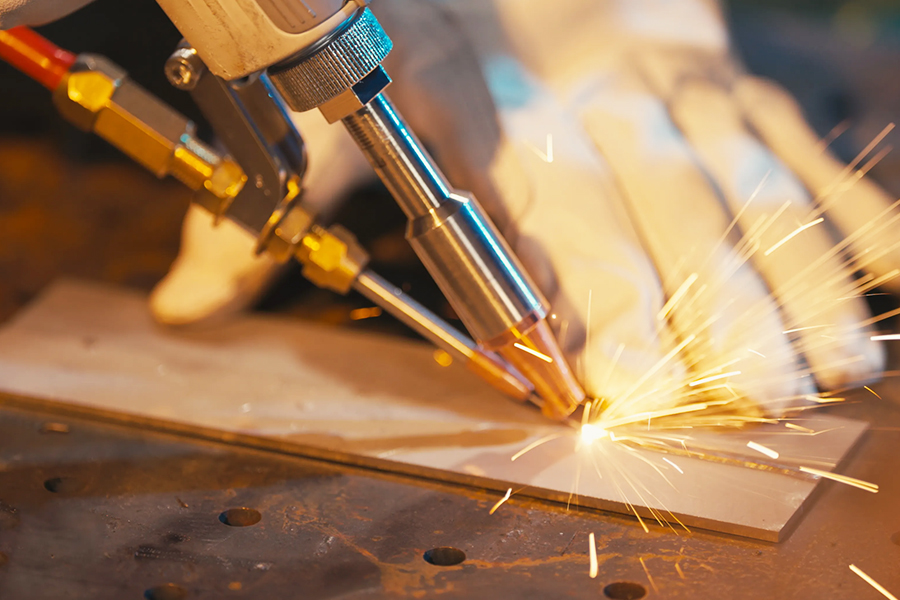

Future Trends in Micro Laser Welding
1. AI-Driven Welding Systems
Artificial intelligence is set to revolutionize micro laser welding by enabling real-time monitoring and adaptive control for unparalleled accuracy.
2. Integration with Robotics
Automating the welding process with robotics increases consistency and reduces human error.
3. Advancements in Beam Technology
Emerging laser technologies promise even greater precision and efficiency, expanding the capabilities of micro laser welding.
Final Thoughts
Micro laser welding is a cornerstone of modern manufacturing, offering unmatched precision and versatility. From crafting intricate jewelry to assembling life-saving medical devices, this technology continues to push the boundaries of what’s possible in small-scale welding.
Whether you’re an industry professional or a craftsman, investing in micro laser welding technology is a step toward achieving superior results in less time. The possibilities are limitless, and the future of precision welding is here.

