
Metal Laser Welder: Precision, Efficiency, and Revolution in Welding
In the realm of modern metalworking, the metal laser welder stands as a game-changing innovation. With its ability to deliver precision, speed, and unmatched quality, this technology has become an essential tool across industries. From intricate jewelry crafting to large-scale manufacturing, metal laser welding transforms the way we join materials, ensuring consistency and durability.
Understanding the Metal Laser Welder
A metal laser welder utilizes concentrated laser beams to fuse materials. This process generates intense heat in a focused area, allowing metals to melt and bond with minimal thermal distortion. Compared to traditional welding methods, laser welding offers superior precision, faster operation, and a cleaner finish.
Key features of a metal laser welder include:
• High welding speed.
• Minimal heat-affected zones (HAZ).
• Compatibility with diverse materials, including thin metals and alloys.
Why Choose a Metal Laser Welder?
1. Unmatched Precision
The focused laser beam delivers sub-millimeter accuracy, making it ideal for detailed work and delicate materials.
2. Speed and Efficiency
Metal laser welders complete tasks in a fraction of the time required by traditional methods, increasing overall productivity.
3. Enhanced Weld Quality
Laser welding produces clean, defect-free joints with minimal porosity, reducing the need for post-weld finishing.
4. Eco-Friendly Operation
Laser welders consume less energy and generate minimal waste, aligning with sustainable manufacturing practices.

Applications of Metal Laser Welders
1. Automotive Industry
Metal laser welders are indispensable in automotive manufacturing, where precision and efficiency are paramount. From chassis components to battery casings, laser welding ensures durability and safety.
2. Aerospace Engineering
In aerospace, lightweight materials like aluminum and titanium demand precise welding. Metal laser welders meet these requirements, enabling the creation of high-strength, lightweight components.
3. Electronics Manufacturing
The compact size and intricate designs of electronic devices make laser welding a preferred method for joining delicate components.
4. Jewelry and Artistic Metalwork
Artisans use metal laser welders to craft intricate designs and make seamless repairs, elevating the quality of their creations.
5. Medical Device Fabrication
In the medical field, laser welding produces sterile, high-precision joints for surgical instruments and implants.

How Does Laser Welding Work?
1. Preparation
Before welding, the surface is cleaned to remove contaminants and ensure optimal laser absorption.
2. Laser Beam Application
The laser focuses intense energy on the welding point, creating a molten pool.
3. Solidification
As the molten metal cools, it solidifies into a strong, durable joint.
This process is highly controlled, ensuring consistency across welds and reducing the likelihood of defects.
Advantages Over Traditional Welding
Speed
Laser welders operate at much higher speeds, completing tasks in seconds that might take minutes with traditional methods.
Reduced Heat Impact
The concentrated laser minimizes the spread of heat, preserving the material’s properties and reducing distortion.
Material Compatibility
From stainless steel to exotic alloys, metal laser welders handle a wide range of materials with ease.
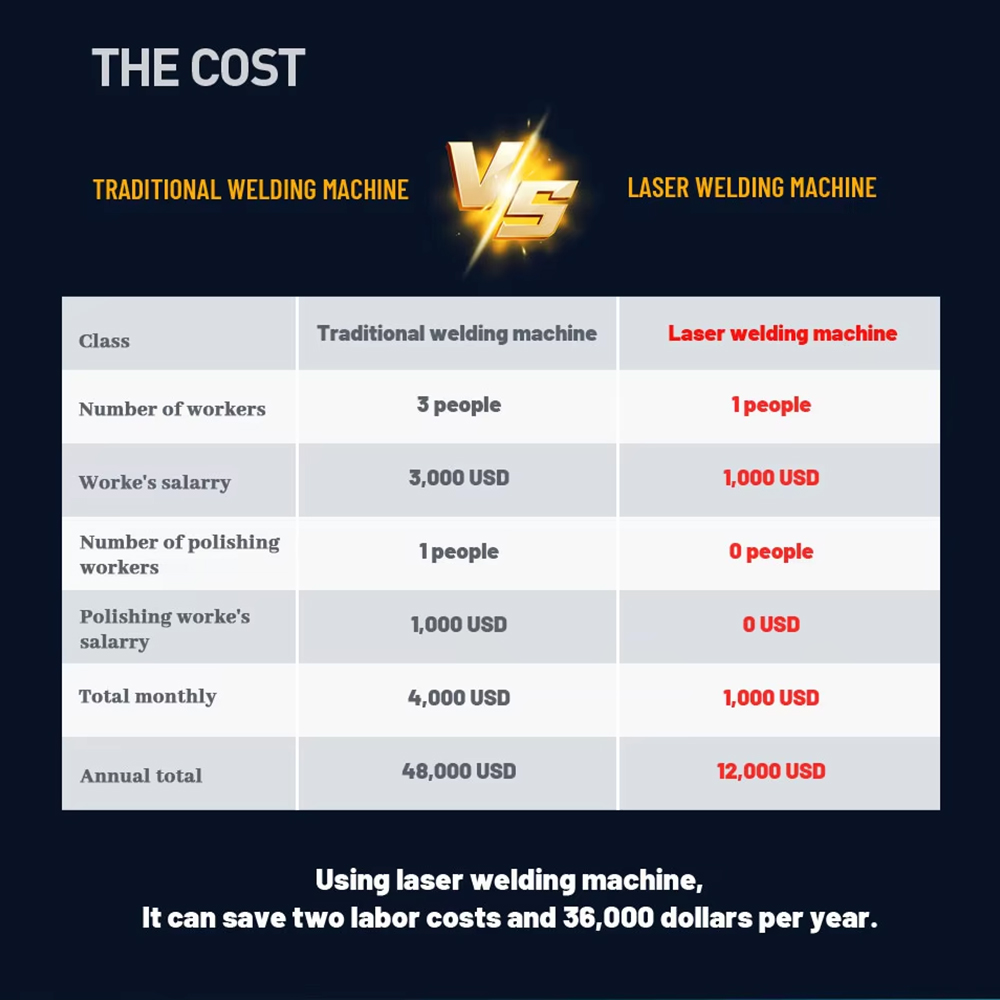
Cost Savings
Despite a higher initial investment, the efficiency and reduced waste of laser welding lead to significant long-term savings.
Choosing the Right Metal Laser Welder
1. Power Output
Higher wattage enables deeper penetration and faster welding speeds, ideal for industrial applications.
2. Beam Quality
A consistent, high-quality beam ensures precise welds, particularly for thin or intricate materials.
3. Cooling Systems
Effective cooling mechanisms prevent overheating and extend the lifespan of the machine.
4. Automation Features
Advanced models integrate automation, allowing for hands-free operation and greater consistency.
Safety Considerations
Laser welding involves high-intensity beams and requires proper safety measures:
• Protective Gear: Operators should wear laser-rated eyewear to shield against harmful radiation.
• Ventilation: Proper airflow prevents the accumulation of fumes and particulates.
• Training: Comprehensive training ensures safe and efficient operation of laser welding equipment.
Economic and Environmental Impact
Cost Efficiency
The initial investment in a metal laser welder is offset by long-term savings in labor, materials, and energy.
Sustainability
Laser welding’s reduced waste and lower energy consumption support eco-friendly manufacturing practices.
Increased Productivity
Faster welding speeds and minimal post-processing requirements improve throughput, making operations more profitable.
Future Trends in Metal Laser Welding
AI Integration
Artificial intelligence is poised to revolutionize laser welding by enabling real-time monitoring and adaptive control.
Enhanced Portability
Smaller, lightweight designs are making laser welders accessible for on-site applications and smaller workshops.
Advanced Materials
Ongoing research into new laser technologies will expand the range of materials compatible with laser welding.
Closing Thoughts
The metal laser welder is more than a tool—it’s a gateway to precision, efficiency, and innovation. Whether you’re a large-scale manufacturer or a craftsman, this technology empowers you to achieve flawless results in less time. By investing in a metal laser welder, you’re not only enhancing your capabilities but also aligning with the future of sustainable and advanced manufacturing.
Explore the possibilities today and elevate your metalworking projects to new heights. The future of welding is here, and it’s powered by lasers.



