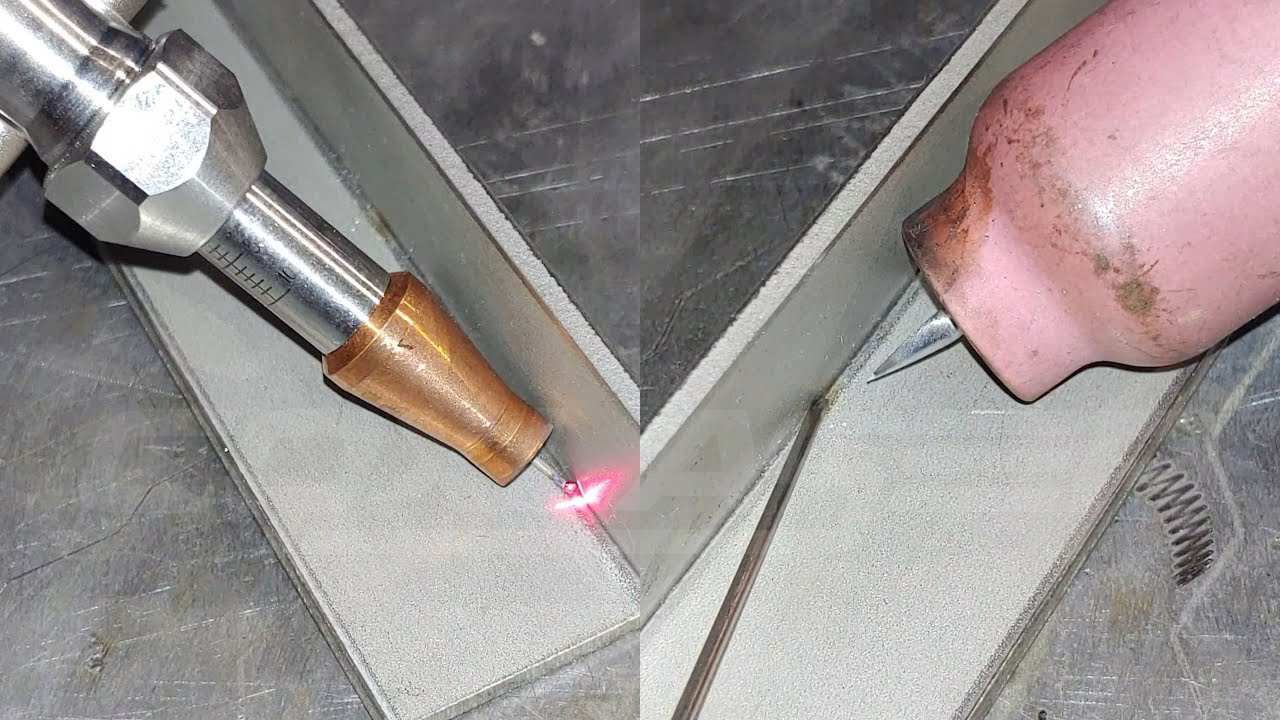
Laser Welding vs TIG Welding: A Comprehensive Comparison
When it comes to precision welding, the debate between laser welding vs TIG welding often arises. Both methods are staples in metal fabrication, yet they serve distinct purposes depending on the application, material, and desired outcome. Laser welding is known for its speed and precision, while TIG welding offers versatility and control. Understanding the strengths and limitations of these techniques can help manufacturers, engineers, and craftsmen make informed decisions.
What is Laser Welding?
Laser welding uses a concentrated laser beam to melt and fuse materials. This method is ideal for applications requiring high precision and minimal thermal distortion. Its advantages include:
• High welding speeds.
• Minimal heat-affected zones (HAZ).
• Consistent weld quality.
Laser welding is often used in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and electronics, where precision and efficiency are paramount.

What is TIG Welding?
TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) welding involves a tungsten electrode to create the weld while shielding the area with inert gas, typically argon. This method provides excellent control and versatility, allowing for intricate welding tasks. TIG welding is commonly used for:
• Thin materials.
• Complex shapes.
• Aesthetic welds requiring minimal cleanup.
Though slower than laser welding, TIG welding excels in applications where precision craftsmanship is valued.
Key Differences Between Laser Welding and TIG Welding
1. Speed and Efficiency
• Laser Welding: Offers unmatched speed, making it suitable for high-volume production.
• TIG Welding: Slower due to manual operation, but ideal for detailed work.
2. Precision
• Laser Welding: Achieves micron-level accuracy, making it perfect for delicate or intricate parts.
• TIG Welding: Provides good control, though not as precise as laser welding.
3. Heat-Affected Zone (HAZ)
• Laser Welding: Minimal HAZ reduces material distortion and preserves the base material’s properties.
• TIG Welding: Larger HAZ increases the risk of warping, particularly on thin materials.
4. Material Compatibility
• Laser Welding: Handles a wide range of materials, including dissimilar metals, with ease.
• TIG Welding: Versatile but may require additional preparation for certain materials.
5. Cost
• Laser Welding: Higher initial investment but lower operational costs due to efficiency.
• TIG Welding: Lower equipment costs but higher labor expenses due to slower operation.

Applications: Where Each Method Excels
Laser Welding
1. Aerospace: Precision welding for lightweight, high-strength components.
2. Automotive: Fast and efficient assembly of car parts and battery packs.
3. Medical Devices: Clean, precise welds for surgical instruments and implants.
4. Electronics: Joining tiny components without damaging sensitive materials.
TIG Welding
1. Artistic Metalwork: Ideal for custom designs requiring manual craftsmanship.
2. Construction: Welding structural elements and decorative fixtures.
3. Repair Work: Fixing cracks and worn parts with precision.
4. Food and Beverage: Creating sanitary welds for stainless steel equipment.
Choosing Between Laser Welding and TIG Welding
Factors to Consider:
1. Project Scale: Laser welding suits large-scale production, while TIG welding is better for small, detailed projects.
2. Material Type: Both methods handle a range of materials, but laser welding excels with thin and delicate metals.
3. Budget: Consider the trade-off between initial investment and operational costs.
4. Skill Level: TIG welding requires skilled operators, whereas laser welding benefits from automation.
Innovations in Welding Technology
AI Integration
Artificial intelligence is transforming both methods, enabling real-time adjustments and error detection for optimal performance.
Hybrid Techniques
Combining laser and TIG welding creates hybrid processes that leverage the strengths of both methods for specialized applications.
Portable Equipment
Compact and portable systems are making both techniques more accessible to small businesses and fieldwork operations.
Economic and Environmental Impact
Laser Welding
• Economic: Reduces waste and labor costs, providing long-term savings.
• Environmental: Lower energy consumption and minimal material waste make it eco-friendly.
TIG Welding
• Economic: Affordable for small-scale operations but less cost-effective for high-volume production.
• Environmental: Uses more energy but offers recyclable components.
Safety Considerations
Laser Welding
1. Wear laser-rated protective eyewear.
2. Operate in a controlled environment with proper shielding.
3. Ensure regular equipment maintenance to avoid hazards.
TIG Welding
1. Protect against UV and infrared radiation with welding helmets.
2. Use proper ventilation to avoid inhaling harmful fumes.
3. Inspect cables and gas lines for leaks or damage.
The Future of Welding: Laser vs TIG
As industries evolve, the demand for precise, efficient, and sustainable welding methods continues to grow. While laser welding dominates high-tech applications, TIG welding remains irreplaceable in artistic and detailed craftsmanship. Future developments, such as AI-driven welding systems and advanced beam technologies, promise to enhance both methods, making them even more versatile and effective.
Each method has its strengths, and understanding their differences is key to selecting the best approach for your project. Whether speed, precision, or craftsmanship is your priority, there’s a welding solution tailored to your needs.


